python
python
Is a both
compiled & interpreted object-oriented high-level programing language with
dynamic sensa tics.
Python
is one of the easiest yet most useful programming languages
Competitive
Programming, Web Development, and creating software
Today, Python
is used in all kinds of development from game
development, basic programming, and scripting to large
and complex software development.
Creator of
python
Python was
developed by 1991 by a data programmer Guido Ven Rossum
Name python
the British Sketch comedy Series Monty python
flying cercus or which he was big fan .’
Python 2.o
was released in 2000 python 3.0 released
in 200008
It has a large
community support and is rich in the library, having all kinds of frameworks for backend, frontend
Feature:
OOPs Dynamically
type GUI programming support extensible large stand and library free & open Source
Cross
platform language interpreted
Easy to
learn & us expressive language
Application
Data Science
Web
Development
Data
engineering
ML
AI
Data analytics
First program
in python
To call first function in python we just need to write print followed
by parentheses () and various inside question marks
INPUT:
Print (“hello
world”)
Output: hello
World
using multiple line in python
These are two
methods to write statement in multiple line
To print multiple line
in python triple question are used \n backspace is used to insert Something in
the next line
print(“hello world”)
print(“hello \n world”)
Comment in python:
Single line Comment:
To add single line Comment #hash is used python completely
ignore anything written after #
# in this program I
will add two number
Multiple line
Variable:
In a place holder which container that hole data inside it as
a value
INPUT The world:
A =”hello world”
Print(a)
Output:
Hello world
Rule of Variable:
Python is a case sensitive language therefore variable name
are sensitive as well
A =” hello”
Print(a)
I will throw an error as a case used here for variable
name
Make sure to not use space while creating a variable one we
can use underscore to separate a name while writing a variable.
A variable name should never start with a number
or Special Symbol
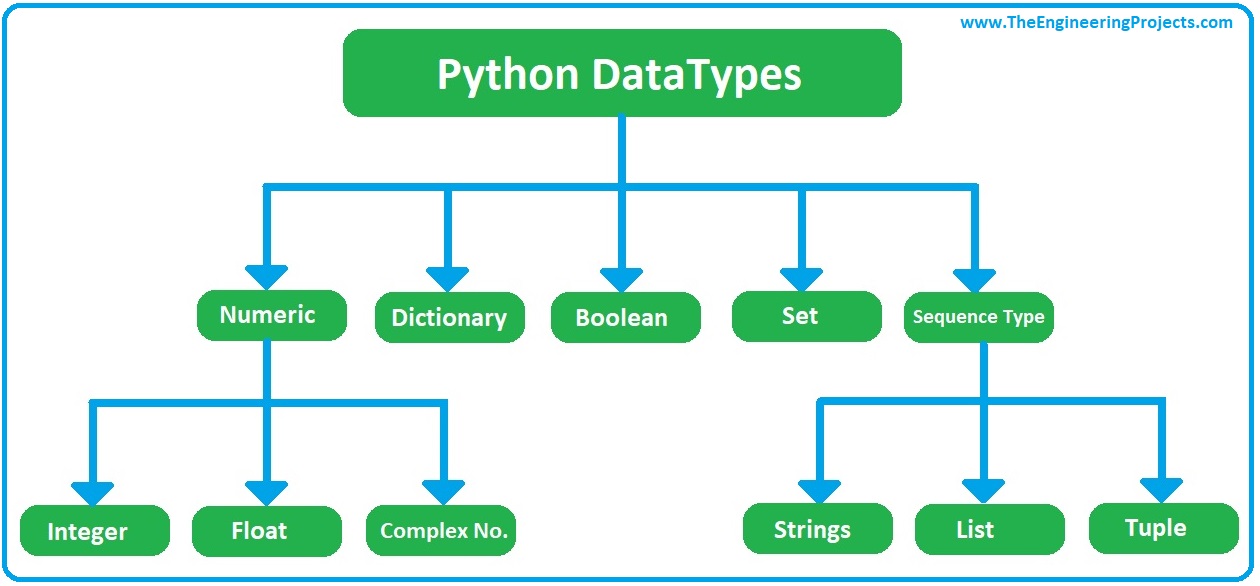
Data type & use input:
Text type: string(str)
Numeric type( int, float, complex
Sequence type: list tuple & Range
Mapping: Dictionaries (Duct)
Set type: set, frezenest
Bolean type: bool
Byte: byte array ,
type view & Binary type
User input: to ask the input from the user default data type
string
Input: name : input(“enter your name here”)
Print(name)
Example:
Name = (input (“enter your name “))
Print (name)
Age = (input (“enter your age “))
Print (age)
Type Casting:
Subtype:
Conversion of one data type to another data type
Thera are two types of caseing:
Input type conversion:
when python itself convert one data type to another
Explicit type conversion when user convert one data type to
another.
Operators:
Indicate what
operation is to be perform while operands indicates and what the action or the
operation should be performed
In Python programming, Operators in general are used to
perform operations on values and variables. These are standard symbols used for
logical and arithmetic operations.
X+y
OPERATORS: These are the special
symbols. Eg- + , * , /, etc.
OPERAND: It is the value on which the operator
is applied.
In this given expression x , y &0 are operand
Types of operators:
Asthmatic operators:
are used to perform basic mathematical operations like addition, subtraction,
multiplication and division.
Comparison operators:
compares the values. It either returns True or False according to the
condition.
Logical operator:
perform Logical
AND, Logical OR and Logical NOT operations.
It is used to combine conditional statements.
The
precedence of Logical Operators in Python is as follows:
1.
Logical
not
2.
logical
and
3.
logical
or
Bitwise
operators:
act on
bits and perform bit-by-bit operations. These are used to operate on binary
numbers.
Bitwise
Operators in Python are as follows:
1.
Bitwise
NOT
2.
Bitwise
Shift
3.
Bitwise
AND
4.
Bitwise
XOR
5.
Bitwise
OR
Assignment
operators:
re used to assign values to
the variables. This operator is used to assign the value of the right side of
the expression to the left side operand.
Identity operators:
both are used to check if two values are located on the same part of the memory. Two variables that are equal do not imply that they are identical.
is True if the operands are
identical
is not True if the operands are not identical
membership operators:
that
are used to test whether a value or variable is in a sequence.
in True if value is found in the
sequence
not
in True if
value is not found in the sequence
conditional operators:
re used
to execute certain blocks of code based on specific conditions. These
statements help control the flow of a program, making it behave differently in
different situations.
allow Computer to execute a certain
canal only if it is true
·
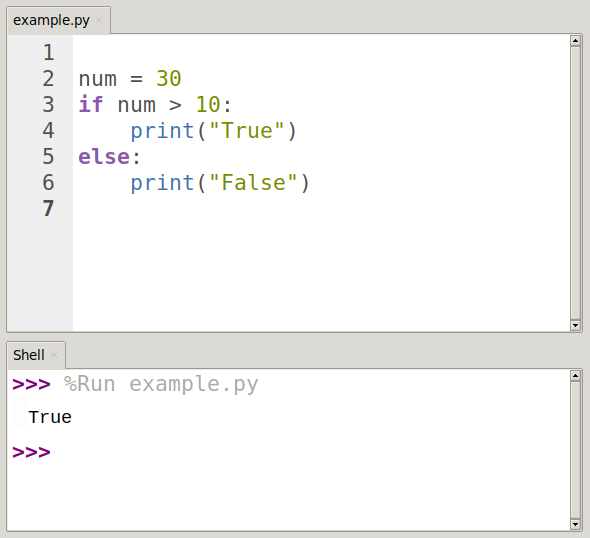
if Statement:
is the
simplest form of a conditional statement. It executes a block of code if the
given condition is true.
If – else:
alows us
to specify a block of code that will execute if the condition(s) associated
with an if or elif statement evaluates to False. Else block provides a way to
handle all other cases that don't meet the specified conditions.
Short hand
if
Short-hand if statement allows us to write a single-line if
statement.
Short Hand
if -else
The
short-hand if-else statement allows us to write a single-line if-else statement.
Elif statement
stands
for "else if." It allows us to check multiple conditions , providing
a way to execute different blocks of code based on which condition is true.
Using elif statements makes our code more readable and efficient by eliminating
the need for multiple nested if statements.
Loop in python
are used
to repeat actions efficiently.
The main
types are For loops (counting through items) and While loops (based on
conditions). Additionally,
, Nested
Loops allow looping within loops for more complex tasks.
While loop
is
used to execute a block of statements repeatedly until a given condition is
satisfied. When the condition becomes false, the line immediately after the
loop in the program is executed.
Else
clause is only executed when our while condition becomes false. If we break out
of the loop or if an exception is raised then it won’t be executed.
For loop
are used for
sequential traversal. For example: traversing a list string or array etc.
In Python, there is “for in” loop which is similar to for each loop in other
languages. Let us learn how to use for loops in Python for sequential
traversals with examples.
While true:
It is a
infinite loop
To break while loop break Statement are used
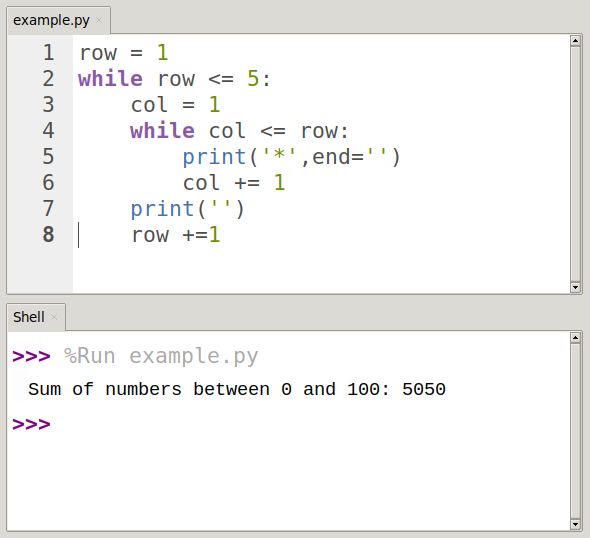
Nested loop
A loop inside
a loop
Nested loop
are also used to solve patten problem
For loop in
conditional Statement
The use of if
else statement increase the ability of a
for loop to computer a task efficiently by use if else statement we can provide
with special condition inside for loop
Block &
continue :
Continue Statement
:
Is used to when
you want to skip a particular condition
Break
Used when you
want to display a loop a certain condition
Is a combination
of number Symbol & latter enclose inside question
Creation of an
String:
String are
created by enclose number latter symbol inside doble question
A = “hello
world”
Print(A)
Print(type(A))
· A = “hello”
· Print(Len(A))
· Print(A. count(“h”))
· Print(A.upper())
· Print(A.lower())
· Print(a.index())
· Print(A.capatalize())
· Print(a.find())
String function
§ Isalphanum
§ Isalpha
§ Isdecimal
§ Isdegit
§ Islower
§ End switch
§ Swap case
§ Strip
§ Split
§ Ljust
§ R just
§ Replace
§ Rindex
List: is a collection of order & Mutable data list and written inside the Seqared bracket the value inside list is separated by comma mutable means one created they can be changed
Mutable datatype
can be written inside list
A =[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
Print ((2))
Print(a[1:6])
Print(a[:6])
Print(a[1:])
Print(a[:::2])
Print(a[-3:-1])
Print(a[:: -1])
Print(a[-1:-5])
Iteration
An iterator in Python is an object that holds a sequence of values and provide sequential traversal through a collection of items such as lists, tuples and dictionaries. . The Python iterators object is initialized using the iter() method. It uses the next() method for
iteration.
1.
__iter__(): __iter__() method initializes
and returns the iterator object itself.
2.
__next__(): the __next__() method retrieves the
next available item, throwing a StopIteration exception when no more items are
available.
Difference between Iterator and Iterable
Iterables
are objects that can return an iterator. These include built-in data structures
like lists, dictionaries, and sets. Essentially, an iterable is anything you
can loop over using a for loop. An iterable implements the __iter__() method,
which is expected to return an iterator object.
Iterators
are the objects that actually perform the iteration. They implement two
methods: __iter__() and __next__(). The __iter__() method returns the iterator
object itself, making iterators iterable as well.
Creating an iterator
Creating
a custom iterator in Python involves defining a class that implements the
__iter__() and __next__() methods according to the Python iterator protocol.
·
Define the Class: Start by defining a class that will act as
the iterator.
·
Initialize Attributes: In the __init__() method of the class,
initialize any required attributes that will be used throughout the iteration
process.
·
Implement __iter__(): This method should return the iterator object
itself. This is usually as simple as returning self.
·
Implement __next__(): This method should provide the next item in the
sequence each time it’s called.
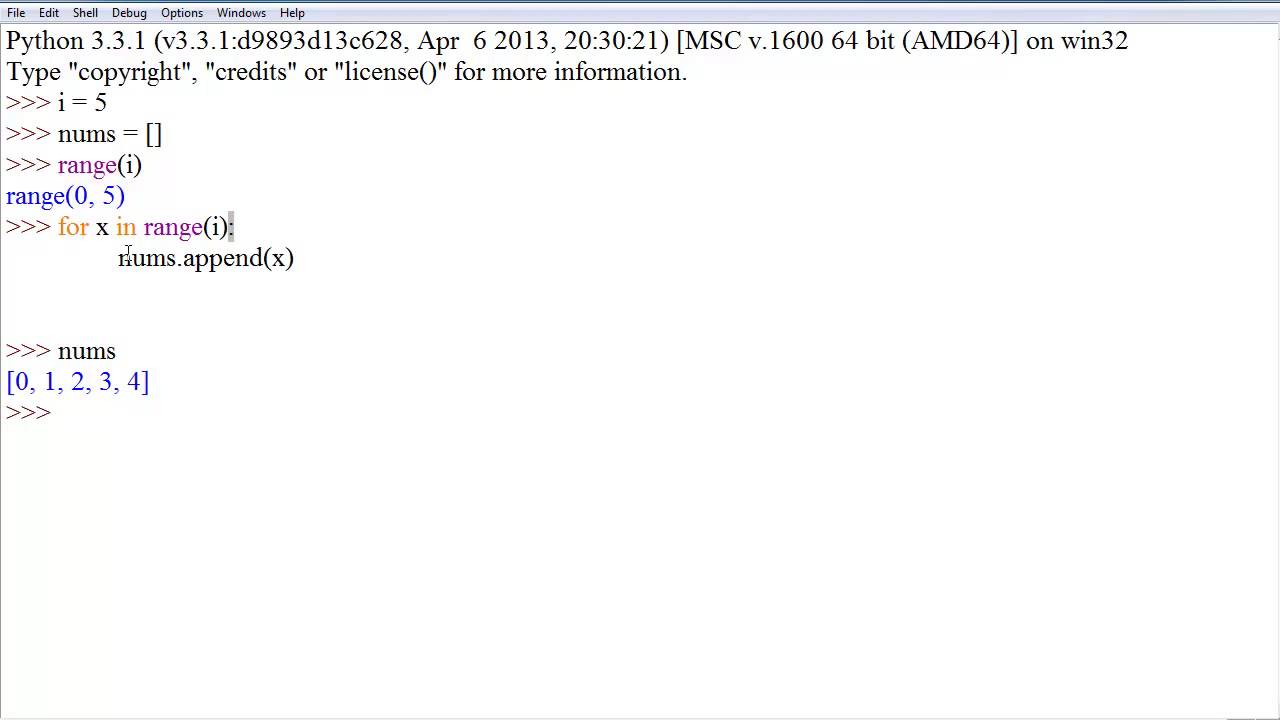
For loop :
A =[1,2,3,4,5,6,7.8]
For I in a:
Print(i)
For I in
range(len(a))
Print(a[i])
While loop :
I =0
While (i<length(a)
Print(a[i])
I+=1
Short hand for
loop :
(print(p) for I
in a )
Function:
A =[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]
Print(a)
Print(len(a))
Print(a.count(5))
a.apppand(9))
print(a)
a.insert[10,7]
print(a)
a.reverse(5)
print(a)
copy
access
extend
Short
Clear
reverse
Tuple :
Are the collection
of order & unmeetable data
For tuple no bracket
are mandatory But choose we can use
parentheses
The value
inside tuple is separated by comma
One created
tuple cannot be changed
Multiple datatype
can be written inside a tuple
slicing is a technique to extract a sub-part of a tuple. It
uses a range of indices to create a new tuple from the original tuple.
Multiple assignment using a Python tuple
You’ve
seen something called tuple unpacking in the previous topic. There’s another
way to unpack a tuple, called multiple assignment. It’s something that you see
used a lot, especially when returning data from a function, so it’s worth
taking a look at this.
Indexed access
We
can access a tuple using index numbers like [0] and [1]:
Append to a Python Tuple
Because
a tuple is immutable, you can not append data to a tuple after creating it.
For the same reason, you can’t remove data from a tuple either. You can, of
course, create a new tuple from the old one and append the extra item(s) to it
this way:
Get tuple length
The len() function works on Python tuples just like it works
on all other iterable types like lists and strings:
Python Tuple vs List
The
most significant difference between a Python tuple and a Python list is that a
List is mutable, while a tuple is not. After defining a tuple, you can not add
or remove values. In contrast, a list allows you to add or remove values at
will. This property can be an advantage; you can see it as write protection. If
a piece of data is not meant to change, using a tuple can prevent errors. After
all, six months from now, you might have forgotten that you should not change
the data. Using a tuple prevents mistakes.
Dictionaries in Python
s a data
structure that stores the value in key: value pairs. Values in a dictionary can be of any data type and can be
duplicated, whereas keys can’t be repeated and must be immutable.
Example: Here, The data is stored in key:value pairs in dictionaries, which
makes it easier to find values.
dictionary
can be created by placing a sequence of elements within curly {} braces, separated by a ‘comma’.
·
From
Python 3.7 Version onward, Python dictionary are Ordered.
·
Dictionary
keys are case sensitive: the same name but different cases of Key will be treated distinctly.
·
Keys
must be immutable: This
means keys can be strings, numbers, or tuples but not lists.
·
Keys
must be unique: Duplicate
keys are not allowed and any duplicate key will overwrite the previous value.








Comments
Post a Comment