Problem Solving and Searching Techniques:
Problem
Solving and Searching Techniques:
AI is used a lot today It has many advantages and disadvantages AI is a problem which comes in different forms It has some problems which even AI cannot solve because AI was neither made by humans nor by humans AI problems exhibit distinct characteristics that shape the strategies and techniques used to tackle them
effectively. In this article, we delve into the fundamental features of AI
problems, shedding light on what makes them so fascinating and formidable
Problem
solving: is like a park which solves no matter how big the problem instantly.
It solves the problem instantly no matter how big it is..
search space
: search space is the space which is
used to solve the problem in all the studies It covers a range of options that
an agent can choose from to reach the same destination.
Production
Systems
Every automatic
system with a specific algorithm must have rules for its proper functioning and
functioning differently. The production systems in artificial intelligence are
rules applied to different behaviors and environments.
, a production
system refers to a type of rule-based system that is designed to provide a
structured approach to problem solving and decision-making. This framework is particularly
influential in the realm of expert systems, where it simulates human
decision-making processes using a set of predefined rules and facts.
1.
Input: A healthcare professional inputs the
symptoms into Medi Diagnose.
2.
Processing:
·
Medi
Diagnose reviews its
knowledge base for rules that match the given symptoms.
·
It
identifies several potential conditions but recognizes a strong match for
meningitis based on the combination of symptoms.
3.
Output:
·
The
system suggests that meningitis could be a possible diagnosis and recommends
further tests to confirm, such as a lumbar puncture.
·
It
also provides a list of other less likely conditions based on the symptoms for
comprehensive differential diagnosis.
Water
Jug Problem,
is a classic puzzle
in artificial intelligence (AI) that involves using two jugs with different
capacities to measure a specific amount of water
t is a popular
problem to teach problem-solving techniques in AI,
explore
the Water Jug Problem, its significance in AI, and how search algorithms like
Breadth-First Search (BFS) and Depth-First Search (DFS) can be used to solve
it.
typically
involves two jugs with different capacities. The objective is to measure a
specific quantity of water by performing operations like filling a jug,
emptying a jug, or transferring water between the two jugs. The problem can be
stated as follows:
·
You
are given two jugs, one with a capacity of X liters and the
other with a capacity of Y liters.
·
You
need to measure exactly Z liters of water using these two
jugs.
·
The
allowed operations are:
o Fill one of the jugs.
o Empty one of the jugs.
o Pour water from one jug into another
until one jug is either full or empty.
Applications of the Water Jug Problem
Although
the Water Jug Problem itself is a theoretical puzzle, its principles apply to
real-world problems, such as:
·
Managing resources
under constraints, like liquid distribution in a refinery or industrial
process.
·
Puzzle-solving
AI: Similar problems can be
found in robotics, where robots must handle tasks with limited resources and
defined constraints.
·
Game
theory: The problem also serves
as a model for certain types of decision-making tasks in game theory and
optimization.
Strategic
Control
The strategy’s effectiveness and success will depend on how well
it is executed. In organizations, top management ensures its implementation by
exercising Strategic
Control.
Definition: Strategic control
is the forward-looking evaluation process focused towards monitoring, measuring and managing the execution of formulated strategies and making necessary
adjustments.
Breadth First Search, \
In artificial intelligence,
the Breadth-First Search (BFS) algorithm is an essential tool for exploring and
navigating various problem spaces. By systematically traversing graph or tree
structures, BFS solves tasks such as pathfinding, network routing, and puzzle
solving. This article probes into the core concepts of BFS, its algorithms, and
practical applications in AI.
The Breadth-First Search is a
traversing algorithm used to satisfy a given property by searching the tree or graph data structure.
·
Originally
it starts at the root node, then it expands all of its successors, it
systematically explores all its neighbouring nodes before moving to the next
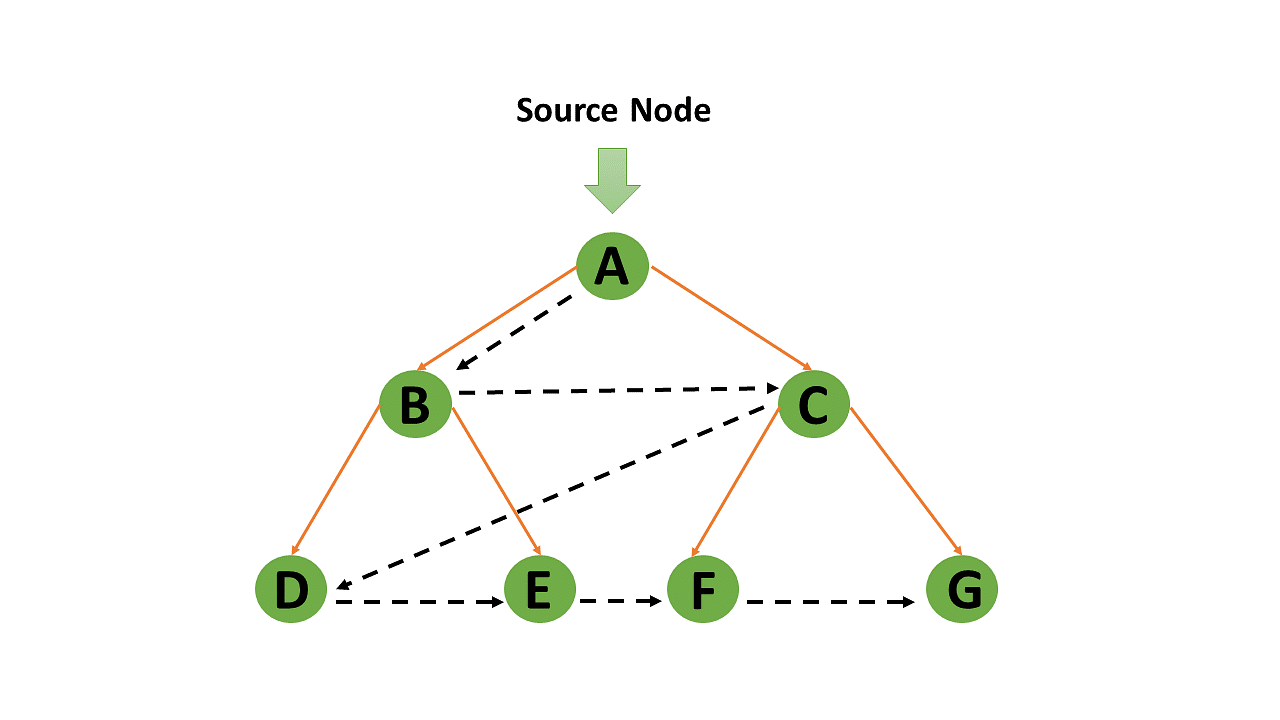
level of nodes. ( As shown in the above image, It starts from the root node A
then expands its successors B)
·
This
process of extending the root node’s immediate neighbours, then to their
neighbours, and so on, lasts until all the nodes within the graph have been
visited or until the specific condition is met. From the above image we can
observe that after visiting the node B it moves to node C. when the level 1 is
completed, it further moves to the next level i.e 2 and explore node D. it will
move systematically to node E, node F and node G. After visiting the node G it
will terminate.
Uniformed search technique
FIFO(QUEUE)
Complete
Optimal
Time complexity
It go to travel by travel
shortest node
Depth first node
Depth-first search contributes
to its effectiveness and optimization in artificial intelligence. From
algorithmic insights to real-world implementations, DFS plays a huge role in
optimizing AI systems. Let's dive into the fundamentals of DFS, its
significance in artificial intelligence, and its practical applications.
a traversing algorithm
used in tree and graph-like data
structures. It generally starts by exploring the deepest node in the frontier.
Starting at the root node, the algorithm proceeds to search to the deepest
level of the search tree until nodes with no successors are reached. Suppose
the node with unexpanded successors is encountered then the search backtracks
to the next deepest node to explore alternative paths.
Uniformed
Stack (FIFO)
Deepest node
Incomplete
Non-optimal
Time complexity
Hill
climbing and its variation
Local
search algorithms
Greedy
approach
Envolve
the initial state
Loop
until a solution is found or there are
No option
left
Select
& apply a new operator
If batter
than current state than it is a new current state
Problem:
Local
maximum
Problem/flat
maximum
Ridge
What is the Heuristic Method?
A heuristic method is an
approach to finding a solution to a problem that originates from the ancient
Greek word ‘eureka’, meaning to ‘find’, ‘search’ or ‘discover’. It is about
using a practical method that doesn’t necessarily need to be perfect. Heuristic
methods speed up the process of reaching a satisfactory solution.
Previous
experiences with comparable problems are used that can concern problem
situations for people, machines or abstract issues. One of the founders of
heuristics is the Hungarian mathematician who published a book about the subject in 1945
called ‘How to Solve It’. He used four principles that form the basis for
problem solving.
Heuristic
method: Four principles
Pólya describes the following four principles in his book:
1.
try to understand the problem
2.
make a plan
3.
carry out this plan
4.
evaluate and adapt
8 puzzle Problem
Given a 3×3 board with 8 tiles
(each numbered from 1 to 8) and one empty space, the objective is to place the
numbers to match the final configuration using the empty space. We can slide
four adjacent tiles (left, right, above, and below) into the empty space.
8-puzzle
Problem is
a classic sliding puzzle that consists of a 3x3 board with 8 numbered tiles and
one blank space. The goal is to rearrange the tiles to match a target
configuration by sliding the tiles into the blank space. The movement can be in
four directions: left, right, up, and down.
In
this article, we will learn how to solve this using Branch and Bound in C
language.
Input
:
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
5 |
6 |
|
|
7 |
8 |
4 |
Output:
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
5 |
6 |
8 |
|
|
7 |
4 |


Comments
Post a Comment